三款免费的PHP加速器:APC、eAccelerator、XCache比较
一直想找一些关于PHP加速的文章,偶然看到杀客的这篇文章,感觉不错,分享给大家,再此感谢杀客。
A、PHP加速器介绍
PHP加速器是一个为了提高PHP执行效率,从而缓存起PHP的操作码,这样PHP后面执行就不用解析转换了,可以直接调用PHP操作码,这样速度上就提高了不少。
Apache中使用mod_php的请求、响应执行流程:
1、Apache接收请求。
2、Apache传递请求给mod_php。
3、mod_php定位磁盘文件,并加载到内存中。
4、mod_php编译源代码成为opcode树。
5、mod_php执行opcode树。
PHP加速器相应的就是第四步,它的目的就是防止PHP每次请求都重复编译PHP代码,因为在高访问量的网站上,大量的编译往往没有执行速度快呢?所以这里面有个瓶颈就是PHP的重复编译既影响了速度又加载了服务器负载,为了解决此问题,PHP加速器就这样诞生了。
zwei、PHP加速器安装与配置
1、安装配置APC
APC全称是Alternative PHP Cache,官方翻译叫”可选PHP缓存”,它是PHP PECL中的一个扩展,好像是facebook在使用它,下面开始安装(ubuntu环境):
$wget http://pecl.php.net/get/APC-3.0.19.tgz
$tar xvzf APC-3.0.19.tgz
$cd APC-3.0.19/APC-3.0.19
$/usr/local/php/bin/phpize
$./configure –enable-apc –enable-apc-mmap –with-php-config=/usr/local/php/bin/php-config
$machen
$sudo make install
下面我们再配置APC,因为我的PECL扩展路径改变了,所以我得移动下编译好的文件:
$sudo mv /usr/local/php/lib/php/extensions/no-debug-non-zts-20060613/apc.so /usr/local/php/lib/php/extensions/PECL
然后我们再编辑php.ini文件进行配置,请把下面的代码加入到php.ini中即可:
extension_dir = “/usr/local/php/lib/php/extensions/PECL”
extension = apc.so
; APC
apc.enabled = 1
apc.shm_segments = 1
apc.shm_size = 64
apc.optimization = 1
apc.num_files_hint = 0
apc.ttl = 0
apc.gc_ttl = 3600
apc.cache_by_default = on
这样重启apache就会在phpinfo()信息中显示。
2、安装配置eAccelerator
eAccelerator的前身其实是truck-mmcache,因为开发truk-mmcache的人被Zend给招安了,所以开发eAccelerator的人继承了truk-mmcache的一些特性,设计出eAccelerator加速器。安装如下:
$wget http://jaist.dl.sourceforge.net/sourceforge/eaccelerator/eaccelerator-0.9.5.tar.bz2
$tar -jxf eaccelerator-0.9.5.tar.bz2
$cd eaccelerator-0.9.5
$/usr/local/php/bin/phpize
$./configure –enable-eaccelerator=shared –with-php-config=/usr/local/php/bin/php-config
$machen
$sudo make install
$sudo mv /usr/local/php/lib/php/extensions/no-debug-non-zts-20060613/eaccelerator.so /usr/local/php/lib/php/extensions/PECL
将下面代码加入php.ini文件中
extension = eaccelerator.so
; eAccelerator
eaccelerator.shm_size = “16”
eaccelerator.cache_dir = “/tmp/eaccelerator”
eaccelerator.enable = “1”
eaccelerator.optimizer = “1”
eaccelerator.check_mtime = “1”
eaccelerator.debug = “0”
eaccelerator.filter = “”
eaccelerator.shm_max = “0”
eaccelerator.shm_ttl = “0”
eaccelerator.prune_period = “0”
eaccelerator.shm_only = “0”
eaccelerator.compress = “1”
eaccelerator.compress_level = “9”
创建缓存目录,重启apache
$sudo mkdir /tmp/eaccelerator
$sudo chmod 777 /tmp/eaccelerator
$sudo /usr/local/apache/apachectl restart
在phpinfo()检查是否安装成功.
3、安装配置XCache
XCache作为国人自己开发的东西,做小菜鸟的我也感到骄傲,而且XCache无论在速度还是性能上都做的不错。下面就赶紧让我们品尝它吧!
$wget http://xcache.lighttpd.net/pub/Releases/1.2.2/xcache-1.2.2.tar.gz
$tar xvzf xcache-1.2.2.tar.gz
$cd xcache-1.2.2
$/usr/local/php/bin/phpize
$./configure –enable-xcache –enable-xcache-coverager –with-php-config=/usr/local/php/php-config
$machen
$sudo make install
$sudo mv /usr/local/php/lib/php/extensions/no-debug-non-zts-20060613/xcache.so /usr/local/php/lib/php/extensions/PECL
在php.ini添加配置信息:
extension = xcache.so
; xcache
xcache.admin.user = “admin”
xcache.admin.pass = “(执行) echo ’(你的密码)’|md5sum(得出的密文)”
;
xcache.size = 24M
xcache.shm_scheme = “mmap”
xcache.count = 2
xcache.slots = 8k
xcache.ttl = 0
xcache.gc_interval = 0
xcache.var_size = 8M
xcache.var_count = 1
xcache.var_slots = 8k
xcache.var_ttl = 0
xcache.var_maxttl = 0
xcache.var_gc_interval = 300
xcache.test = Off
xcache.readonly_protection = On
xcache.mmap_path = “/tmp/xcache”
xcache.coredump_directory = “”
xcache.cacher = On
xcache.stat = On
xcache.optimizer = Off
;
xcache.coverager = On
xcache.coveragedump_directory = “”
创建缓存目录,重启apache
$sudo mkdir /tmp/xcache
$sudo chmod 777 /tmp/xcache
$sudo /usr/local/apache/bin/apachectl restart
去查看phpinfo()信息吧!
drei、PHP加速器测试
1、测试环境
硬件: AMD Athlon 64 X2 Dual Core Processor 4400+ @ 2.2GHz CPU, 2GB 内存. 160GB SATA 硬盘
软件: Linux Ubuntu server Gutsy 7.10, Apache 2.2.4, MySQL 5.0.45 和 PHP 5.2.3
测试指令: ab -c5 -n3000 http://example.com/ (我们使用的是Apache Benchmark (ab) 工具,并发连接为5,3000次请求)
2、测试结果
无任何加速器:
Document Path: /
Document Length: 21757 Bytes
Concurrency Level: 5
Time taken for tests: 288.255212 seconds
Complete requests: 3000
Failed requests: 0
Write errors: 0
Total transferred: 66777000 Bytes
HTML transferred: 65271000 Bytes
Requests per second: 10.41 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 480.425 [Frau] (mean)
Time per request: 96.085 [Frau] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 226.23 [Kbytes/sec] received
Connection Times (Frau)
min mean[+/-sd] median max
Connect: 0 0 0.5 0 19
Processing: 181 479 186.0 444 1822
Waiting: 166 461 184.7 427 1708
Total: 181 479 186.0 444 1822
Percentage of the requests served within a certain time (Frau)
50% 444
66% 525
75% 577
80% 619
90% 732
95% 819
98% 946
99% 1012
100% 1822 (longest request)
APC加速器:
Document Path: /
Document Length: 21757 Bytes
Concurrency Level: 5
Time taken for tests: 98.530068 seconds
Complete requests: 3000
Failed requests: 0
Write errors: 0
Total transferred: 66777000 Bytes
HTML transferred: 65271000 Bytes
Requests per second: 30.45 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 164.217 [Frau] (mean)
Time per request: 32.843 [Frau] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 661.84 [Kbytes/sec] received
Connection Times (Frau)
min mean[+/-sd] median max
Connect: 0 0 0.0 0 2
Processing: 58 163 71.2 155 2452
Waiting: 53 158 69.6 150 2329
Total: 58 163 71.2 155 2452
Percentage of the requests served within a certain time (Frau)
50% 155
66% 178
75% 193
80% 204
90% 235
95% 258
98% 285
99% 302
100% 2452 (longest request)
eAccelerator加速器:
Document Path: /
Document Length: 21757 Bytes
Concurrency Level: 5
Time taken for tests: 95.983986 seconds
Complete requests: 3000
Failed requests: 0
Write errors: 0
Total transferred: 66777000 Bytes
HTML transferred: 65271000 Bytes
Requests per second: 31.26 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 159.973 [Frau] (mean)
Time per request: 31.995 [Frau] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 679.39 [Kbytes/sec] received
Connection Times (Frau)
min mean[+/-sd] median max
Connect: 0 0 0.1 0 3
Processing: 57 159 91.3 148 3830
Waiting: 50 152 89.8 142 3704
Total: 57 159 91.3 148 3830
Percentage of the requests served within a certain time (Frau)
50% 148
66% 174
75% 193
80% 205
90% 239
95% 263
98% 289
99% 309
100% 3830 (longest request)
XCache加速器:
Document Path: /
Document Length: 21757 Bytes
Concurrency Level: 5
Time taken for tests: 99.76300 seconds
Complete requests: 3000
Failed requests: 0
Write errors: 0
Total transferred: 66777000 Bytes
HTML transferred: 65271000 Bytes
Requests per second: 30.28 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 165.127 [Frau] (mean)
Time per request: 33.025 [Frau] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 658.19 [Kbytes/sec] received
Connection Times (Frau)
min mean[+/-sd] median max
Connect: 0 0 0.0 0 2
Processing: 59 164 83.4 155 3367
Waiting: 52 156 66.4 148 1802
Total: 59 164 83.4 155 3367
Percentage of the requests served within a certain time (Frau)
50% 155
66% 178
75% 196
80% 206
90% 237
95% 263
98% 287
99% 305
100% 3367 (longest request)
3、结果摘要
| 请求时间(秒) | 单次请求时间(毫秒) | 最大内存占用(MB) | 最小内存占用(MB) | |
| None | 10.41 | 96.08 | 24 | 24 |
| APC | 30.45 | 32.84 | 21 | 21 |
| eAccelerator | 31.26 | 31.99 | 23 | 18 |
| XCache | 30.28 | 33.02 | 29 | 19 |
四、PHP加速器比较结果总结
1、通过测试得出eAccelerator在请求时间和内存占用综合方面是最好的。
2、通过测试得出使用加速器比无加速器在请求时间快了3倍左右。
3、通过各个官方观察,XCache是更新最快的,这也说明最有发展的。
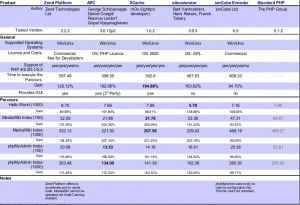
以上是总结结果,你也许会问我到底用那个加速器好呢?我只能告诉你,erste,用一定比不用好,其次每个加速器还有一些可以调优的参数,所以要根据你的系统环境而定,dann,我个人觉得你可以详细研究下eAccelerator和XCache,这两款潜力还是很大的,最后我从比较专业的测试网站搞了一张结果图: